Slow feature analysis (SFA) is a technique for extracting slowly varying freatures from a quickly varying signal in a non-linear fashion. It has been developed in the context of biological modeling, but can also be used to analyze nonstationary time series and estimate underlying driving forces. The figure shows an example of a tent map time series modulated by a slowly varying driving force.

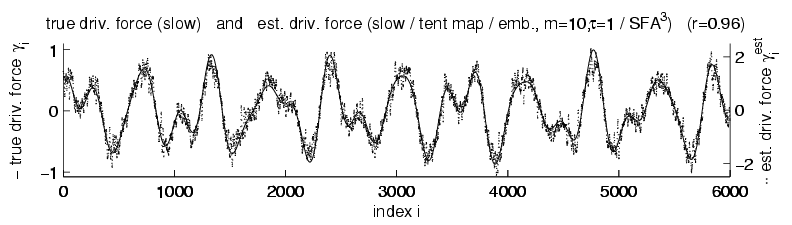
Figure: Estimating the driving force of a tent map time series. Top: Nonstationary times series generated by an iterated tent map with an underlying driving force slowly shifting the 'tent' with cyclic boundary conditions. There is no obvious change of the dynamics. Bottom: True (solid line) and estimated (dots) driving force determined by slow feature analysis.
Python source code for SFA and several other learning algorithms written by Pietro Berkes and Tiziano Zito is available at http://mdp-toolkit.sourceforge.net/.